
Selecting the correct pipe pressure rating is critical for ensuring the safety, durability, and long-term performance of any plumbing, water supply, or industrial pipeline system. Installing a PN10 pipe where a PN16 rating is required can easily result in leaks, burst failures, water damage, and costly system downtime. Because PVC, UPVC pipes, and suction pipe systems each have different structural strengths, choosing the right rating helps avoid these risks while maintaining smooth operation.
Pressure handling varies based on factors like wall thickness, pipe specifications, nominal pipe size, pvc pressure rating, and the system's actual operating pressure and hydrostatic pressure. This guide simplifies how PN10, PN16, and PN20 ratings work and provides practical charts, examples, and selection methods. Whether you’re working on residential plumbing or a high-pressure industrial design, you’ll learn how to choose the right PVC, UPVC, or suction pipe for safe, efficient performance.
What Are Pipe Pressure Ratings?

Pipe pressure rating defines how much internal pressure (in bar) a pipe can safely handle at a standard temperature of 20°C. It serves as a key design and safety parameter for all plumbing pipes, rigid PVC pipes, and UPVC pressure pipes.
“PN” stands for Pressure Nominal, and common classes include PN10, PN16, and PN20. For example, a PN10 pipe can withstand 10 bar of pressure at 20°C. Working pressure refers to the normal condition, while burst pressure is the maximum force a pipe can resist before failure.
Pressure ratings differ based on nominal pipe size and PVC pipe thickness, meaning the same material can handle different pressures depending on wall design and diameter.
Quick Selection Guide
-
PN6: Low-pressure irrigation and garden watering systems.
-
PN10: Ideal for household water supply and basic plumbing pipes.
-
PN16: Common in commercial buildings and medium industrial systems.
-
PN20: Suited for high-rise structures and heavy-duty water applications.
When choosing between UPVC pipe size, UPVC pipe specifications, or rigid PVC pipes, always confirm that the PN class matches your system design and flow requirements.
Rigid PVC Pipes and Their Pressure Ratings
Rigid PVC pipes are widely used in residential, agricultural, and small industrial systems. Their consistent structural strength, lower cost, and corrosion resistance make them ideal for drinking water supply, building distribution lines, underground supply, and general plumbing applications.
The pvc pressure rating depends heavily on the pipe’s wall thickness and diameter. As the pvc pipe thickness increases, the pipe’s ability to handle higher PN ratings also increases.
Rigid PVC Pipe Specifications
|
Size |
PN Rating |
Bar |
Weight/6M (kg) |
Applications |
|
20–32 mm |
PN10 |
10 |
0.7–1.4 |
House connections, fixtures |
|
40–50 mm |
PN10 |
10 |
1.8–2.3 |
Distribution lines, building mains |
|
63–110 mm |
PN10 |
10 |
3.6–11.3 |
Community supply, primary distribution |
Most rigid pvc pipes used for homes operate comfortably under PN10, as municipal supply pressures usually range from 2–5 bar, leaving enough safety margin.
When Do You Need Higher Pressure PVC Pipes?
-
PN16 / PN20 for 20–32 mm: High-pressure pump outlets
-
PN16 for 40–63 mm: Commercial buildings and water mains
-
PN10 / PN16 for 75–200 mm: Industrial transfer lines and distribution networks
Rigid PVC pipes deliver consistent performance across residential and commercial environments when specified correctly for operating pressure and project design.
UPVC Pipes and Plumbing Pressure Ratings
UPVC pipes (Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride) are now preferred for most modern plumbing applications because they are corrosion-free, leak-resistant, and ideal for cold-water supply. These upvc pipes offer higher strength than standard PVC and can safely carry drinking water without any taste or odor contamination.
Most UPVC plumbing pipes use PN10 ratings, which are more than sufficient for municipal supply pressures.
UPVC Plumbing Pipe Specifications
|
Size |
PN Rating |
Bar |
PSI |
Applications |
|
20 mm (½") |
PN10 |
10 |
145 |
Bathroom fixtures, washbasins |
|
25–32 mm |
PN10 |
10 |
145 |
Kitchen lines, house mains |
|
40–50 mm |
PN10 |
10 |
145 |
Larger building supply, overhead tanks |
UPVC pressure pipes perform exceptionally well under normal temperatures. However:
Temperature Consideration
-
PN ratings apply at 20°C
-
At 40°C, UPVC pressure capacity drops by ~20%
-
Do NOT use UPVC for hot water use CPVC or metal pipes instead
This is an important factor when choosing upvc pipe for water supply, especially in warmer regions or rooftop installations.
Suction Pipe Pressure Ratings
A suction pipe works differently from regular pressure pipes. It must withstand both: Internal discharge pressure, and External atmospheric pressure, which tries to collapse the pipe when vacuum suction occurs.
This means suction pipes must be designed for:
-
Higher wall stiffness
-
Vacuum resistance
-
Impact strength
Regular UPVC pipes cannot be used for suction applications, as they may collapse under negative pressure.
Suction pipes are commonly used in:
-
Pump suction lines
-
Agricultural borewell systems
-
Dewatering operations
-
Slurry and sewage handling
Most suction pipes operate within the PN10–PN16 range depending on diameter.
How to Select the Right Pipe Pressure Rating
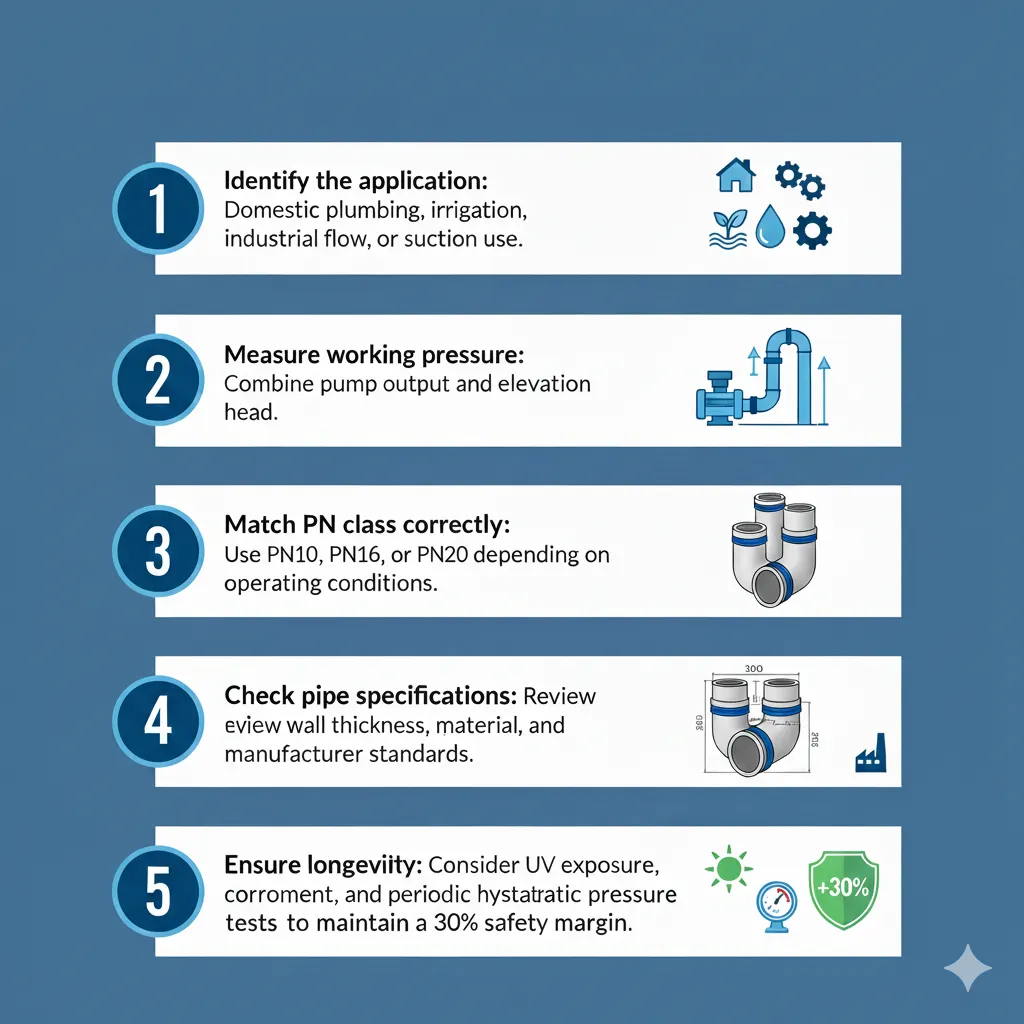
Choosing the correct pipe pressure rating involves several steps to ensure performance and safety:
-
Identify the application: Domestic plumbing, irrigation, industrial flow, or suction use.
-
Measure working pressure: Combine pump output and elevation head.
-
Match PN class correctly: Use PN10, PN16, or PN20 depending on operating conditions.
-
Check pipe specifications: Review wall thickness, material, and manufacturer standards.
-
Ensure longevity: Consider UV exposure, corrosion environment, and periodic hydrostatic pressure tests to maintain a 30% safety margin.
Properly rated pipes reduce maintenance costs and ensure consistent performance over decades.
Pressure Rating Calculation Guide
Calculation Formula
Required PN Rating = (Municipal Pressure + Elevation Head + Pump Pressure) × 1.3
The extra 30% safety factor accounts for surges and long-term usage.
Example – 3-Story Building (PN10)
If the total system pressure sums to around 7 bar (including elevation and pump pressure), applying the 1.3 safety factor gives 9.1 bar, which fits a PN10 pipe rating.
Example – 10-Story Building (PN20)
For a high-rise with total expected pressure near 14 bar, the safety-multiplied requirement is 18.2 bar, making PN20 the correct selection.
Size and Pressure Relationship
The relationship between upvc pipe size and pressure rating is based on structural physics. Smaller diameters can handle higher PN ratings because the wall thickness can be increased more efficiently.
Size vs Pressure Capacity Table
|
Size Range |
Maximum Practical PN |
Reason |
|
20–32 mm |
PN20 |
High wall thickness possible |
|
40–63 mm |
PN16 |
Balanced thickness-to-diameter ratio |
|
75–110 mm |
PN10–16 |
Limits in wall thickness |
|
125–200 mm |
PN6–10 |
Large diameters lower strength |
This is why high-pressure pipelines often use multiple smaller pipes rather than a single large pipe.
Why Scotto Pipes Is the Smarter Choice
Scotto Pipes manufactures a complete range of UPVC pipes, rigid PVC pipes, and suction pipes across PN10, PN16, and PN20 pressure classes, all engineered as per strict IS standards and tested through rigorous hydrostatic pressure procedures. Our pipes maintain consistent wall thickness and follow a zero-defect QC process, resulting in high-pressure tolerance, excellent long-term durability, and complete resistance to corrosion and UV exposure.
Beyond product quality, Scotto Pipes provides strong technical support, including pressure calculation assistance, system design guidance, on-site installation help, and troubleshooting for complex projects. Our full product range covers PN10 for residential plumbing, PN16 for commercial rigid PVC pipes, and PN20 for heavy-duty industrial and high-rise applications, with all major nominal pipe sizes readily available.
With Scotto Pipes, you receive reliable pipe pressure rating performance backed by industry-leading support, certified quality, and long-lasting warranty assurance.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct pipe pressure rating safeguards your plumbing or water system from leaks and premature failure. Always maintain a 30% pressure safety margin and align the PN class, pipe size, and material specifications with your requirements.
-
Use PN10 for residential plumbing.
-
Use PN16 for medium commercial systems.
-
Use PN20 for high-rise and heavy-duty industrial applications.
With Scotto Pipes, users gain the advantage of tested reliability, durability, and full coverage across PVC, UPVC, and suction systems built to endure India’s toughest water conditions.
FAQs
Q1. What does PN stand for in pipe pressure rating?
PN means Pressure Nominal, representing the maximum pressure a pipe can safely handle at 20°C.
Q2. Can UPVC pipes be used for high-pressure applications?
Yes. UPVC pipes with PN16 and PN20 ratings can easily handle medium to high-pressure systems.
Q3. What is the difference between PN10, PN16, and PN20?
They indicate increasing pressure tolerance: PN10 = 10 bar, PN16 = 16 bar, PN20 = 20 bar.
Q4. Are suction pipes rated using PN?
Yes. Heavy-duty suction pipes are generally classified within PN10–PN16 pressure ranges.
Q5. How does wall thickness affect pipe pressure capacity?
Thicker walls increase strength, enabling higher pressure ratings without deformation or burst risk.







